Skin Exfoliation: How to Smooth, Brighten & Protect Your Skin
When working with skin exfoliation, the process of removing dead skin cells from the outer layer to improve texture, tone, and radiance, you’re essentially giving your skin a fresh start. Also known as exfoliation, it supports the skin’s natural turnover and helps other products work better. Think of it as a quick reset button for dull or flaky skin, and you’ll see why it matters for everything from acne to anti‑aging.
Skin exfoliation comes in two main flavors. chemical exfoliation, uses acids or enzymes to dissolve the bonds that hold dead cells together is great for a uniform, deep clean without the harsh scrubbing. physical exfoliation, relies on gritty particles or tools to manually lift away surface cells offers instant gratification and is easy to spot in a product. Within the chemical camp, alpha hydroxy acids (AHA), water‑soluble acids like glycolic or lactic that target surface texture excel at brightening and smoothing, while beta hydroxy acids (BHA), oil‑soluble salicylic acid that penetrates pores to clear congestion are the go‑to for oily or acne‑prone skin. These entities intersect: chemical exfoliation often includes AHAs or BHAs, and physical exfoliation can be combined with gentle enzymes for a balanced routine.
Key Factors to Choose the Right Exfoliant
First, look at your skin type. Dry or sensitive skin usually benefits from low‑strength AHAs or enzyme‑based formulas that avoid irritation. Oily, blemish‑prone skin tends to respond better to BHAs because they dissolve oil and unclog pores. Second, consider the concentration and pH; a product with 10‑12% glycolic acid at a pH of 3.5 is strong enough for regular use, while 2‑5% is safer for beginners. Third, think about frequency. Chemical exfoliants can be applied 2‑3 times a week, whereas physical scrubs should stay under once a week to prevent micro‑tears. Finally, pair exfoliation with hydration. After you strip away dead cells, a barrier‑repair moisturizer with ceramides or hyaluronic acid locks in moisture and reduces post‑exfoliation redness.
Beyond the basics, many readers wonder how exfoliation fits into broader skin goals. If you’re targeting hyperpigmentation, regular AHA use accelerates the fading of dark spots by speeding up cell turnover. For anti‑aging, combining a mild AHA with antioxidants like vitamin C maximizes collagen support while minimizing irritation. And if you’re dealing with occasional breakouts, a BHA‑focused routine can keep pores clear without over‑drying the surrounding skin. The beauty of skin exfoliation is its adaptability: you can mix and match acids, adjust frequency, and layer with serums to fine‑tune results.
Now that you’ve got a clear picture of how chemical and physical methods work, what ingredients to watch for, and how to integrate exfoliation into a broader regimen, you’re ready to explore the specific articles below. Each post dives deeper into product recommendations, step‑by‑step guides, and troubleshooting tips, so you can pick the exact approach that matches your skin’s needs and start seeing smoother, brighter results today.
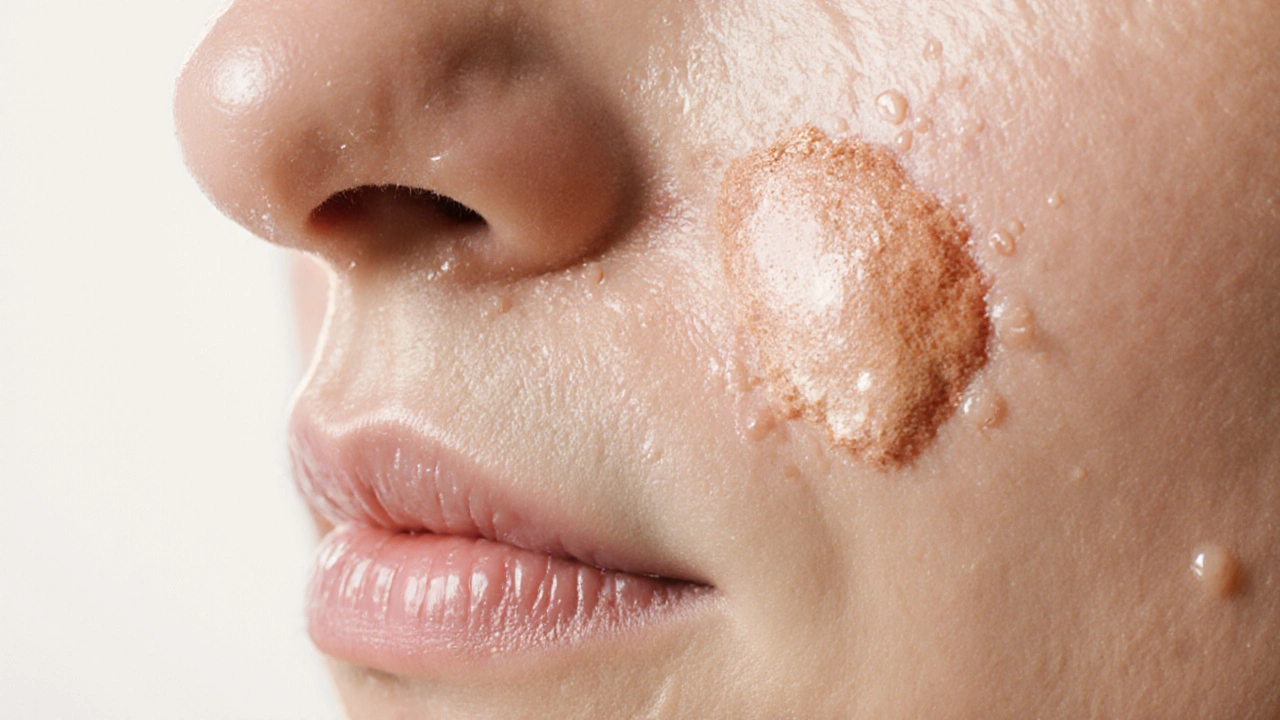

Why Regular Skin Exfoliation Stops Itching - Essential Guide
Learn why regular skin exfoliation prevents itching, how often to do it, which methods suit different skin types, and ways to avoid irritation for smoother, itch‑free skin.